-
Remove
-
Recycle
-
Reuse
-
Reduce
-
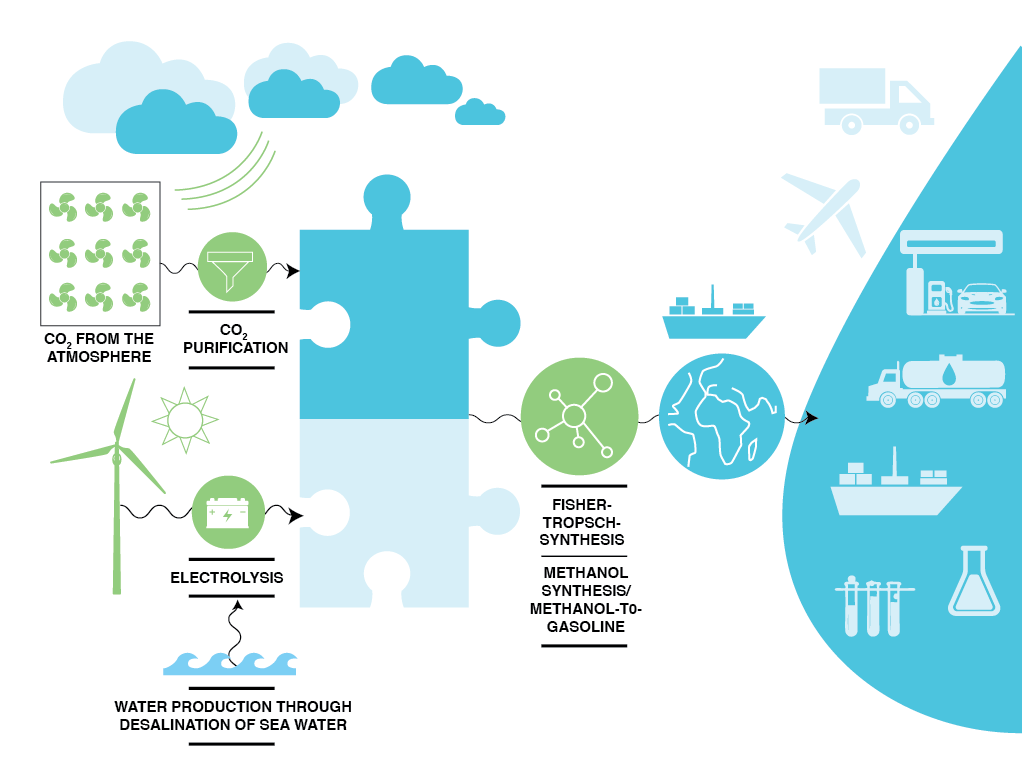
E-FuelsE-fuels are generated exclusively with renewable energy. To put it simply, hydrogen is produced using renewable electricity and then combined with carbon dioxide, e.g. from industrial exhaust gases or from the air, to form a hydrocarbon (Natural Gas) with zero net greenhouse gas emissions. This procedure is now commonly known…Recycle
E-fuels are generated exclusively with renewable energy. To put it simply, hydrogen is produced using renewable electricity and then combined with carbon dioxide, e.g. from industrial exhaust gases or from the air, to form a hydrocarbon (Natural Gas) with zero net greenhouse gas emissions. This procedure is now commonly known by the terms Power-to-X (PtX), Power-to-Liquids (PtL) and Power-to-gas (PtG). Another key advantage is that synthetic fuels are not technically different than their conventional counterparts. They can even be used in classic cars and sold via the existing network of filling stations, and thus gradually blended into existing fuels. The mass balance to produce 1 litre of liquid e-fuel is 3.7–4.5 litres of water, 82–99 MJ of renewable electricity and 2.9–3.6 kg of CO2
- Primary objective of the technology is to generate hydrocarbons with neutral GHG emissions. We are interested in reducing the CO2/GHG emissions from the transportation vehicles
 Where is it deployed?
Where is it deployed?